Have you ever wondered if what you eat can truly influence how you feel mentally? The connection between physical health and mental well-being has garnered much attention in recent years, with many people seeking natural ways to enhance their mood and emotional resilience. One nutrient that often comes into the conversation is collagen. You might be curious: does collagen help with mental health?

This image is property of www.everywomanover29.com.
Understanding Collagen
Collagen is the body’s most abundant protein, playing an essential role in maintaining the structure of your skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Imagine collagen as the glue that holds everything together, providing support and elasticity.
What Is Collagen Made Of?
Collagen is a complex protein composed of amino acids, particularly glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. It is primarily derived from animal sources like skin, bones, and connective tissues. In recent years, collagen supplements have surged in popularity, with many people adding them to their health routines in hopes of improving their physical appearance and overall health.
Types of Collagen
There are several types of collagen in your body, but the main ones include:
- Type I Collagen: Found in skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments; it provides strength and structure.
- Type II Collagen: Primarily located in cartilage, it helps with joint health.
- Type III Collagen: Often found alongside Type I, it supports skin, muscles, and blood vessels.
Each type serves a unique purpose, and understanding them can help you see the broader picture of what collagen does in the body.
The Link Between Collagen and Mental Health
Understanding how collagen impacts mental health requires a deep dive into your body’s complex systems. This connection may not be immediate, but it is certainly fascinating.
The Gut-Brain Connection
Your gut and brain have a profound relationship. You might find it surprising, but a healthy gut can positively influence your mood and mental clarity. Here’s where collagen comes into play. Collagen can help heal the gut lining due to its high glycine content, which plays a role in preventing leaky gut syndrome. When your gut is healthy, you are more likely to experience balanced hormones and neurotransmitters, which are critical for mental health.
Collagen and Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers in your brain that influence various functions, including mood and cognition. Collagen contains amino acids that are precursors to important neurotransmitters. For instance, the amino acid glycine contributes to the synthesis of serotonin, often referred to as the “happiness hormone.” Increased glycine levels may lead to better mood regulation, thereby acting as a potential benefit for mental health.
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can manifest in various ways, both physically and mentally. The presence of collagen in your diet could help combat these feelings. Some studies indicate that collagen may have a calming effect on the nervous system. Ingesting collagen-rich foods or supplements could lead to reduced cortisol levels, diminishing the impact of stress on your body.

This image is property of machine.workado.com.
Sources of Collagen
If you want to incorporate collagen into your routine, consider both dietary sources and supplements.
Dietary Sources
Including collagen-rich foods in your diet can be an efficient way to improve your overall well-being. Here are some foods that might benefit you:
- Bone Broth: Made by simmering animal bones, it is rich in collagen and also provides minerals that nourish your body.
- Chicken Skin: Often discarded, chicken skin is a delicious source of collagen when cooked properly.
- Fish and Fish Skins: Fish often has a high collagen content, especially in the skin.
- Eggs: While eggs don’t contain connective tissue, they provide protein and amino acids critical for collagen synthesis.
- Leafy Greens: Although not direct sources of collagen, greens contain chlorophyll, which may increase the body’s collagen production.
Supplements
If whole foods aren’t your thing, collagen supplements are widely available. They usually come in hydrolyzed forms, which means they’re broken down to make it easier for your body to absorb. Selecting a quality supplement is crucial. Look for:
- Type: Make sure to choose a type suitable for your needs; Type I is great for skin, while Type II supports joints.
- Source: Grass-fed bovine, wild-caught fish, and chicken-sourced collagen are often considered high-quality options.
- Added Ingredients: Some supplements contain vitamins or minerals that may support collagen synthesis, such as Vitamin C.
Other Nutrients That Support Collagen Production
Including collagen in your diet is one aspect, but several other nutrients play a pivotal role in collagen synthesis as well.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis. This antioxidant helps stabilize collagen molecules, making your skin, joints, and bones strong and resilient. Including citrus fruits like oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers can help boost your body’s natural collagen production.
Zinc
Zinc aids in the healing process and plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis. Foods rich in zinc include nuts, whole grains, and legumes. Ensuring you get enough zinc can contribute to your overall well-being.
Copper
Copper is another trace mineral that helps form collagen by creating cross-links between collagen fibers. You can find copper in foods like shellfish, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
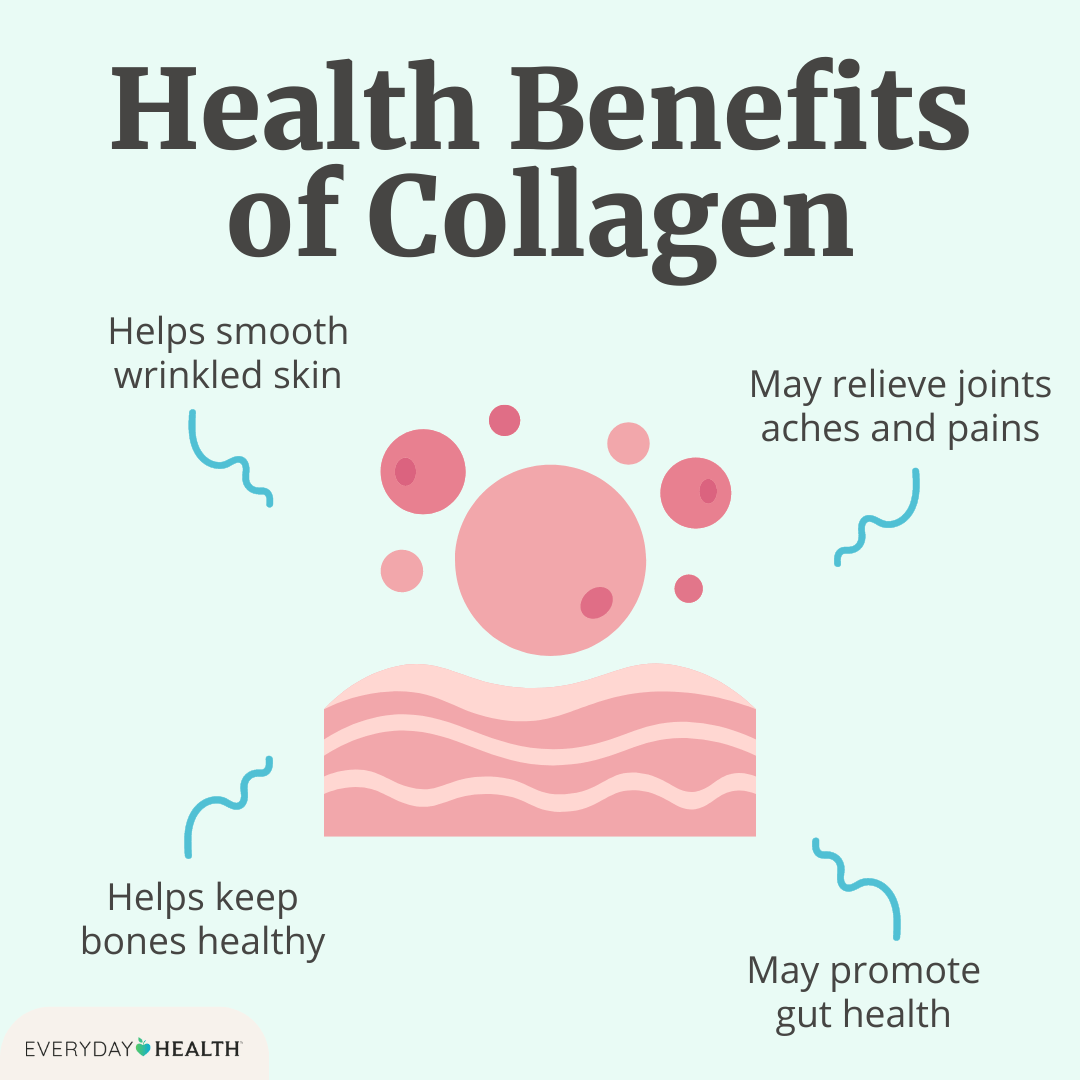
This image is property of images.everydayhealth.com.
Potential Mental Health Benefits
While the relationship between collagen and mental health requires further research, some preliminary benefits have emerged:
Mood Stabilization
High levels of glycine found in collagen may assist in stabilizing your mood. By supporting proper neurotransmitter function, you might find that your emotional swings become less severe. Incorporating collagen into your diet could be a small yet impactful change in how you feel day-to-day.
Improved Sleep Quality
Sleep is vital for your mental health, and certain compounds in collagen might help improve sleep quality. Glycine, in particular, has been shown to promote a better night’s sleep by lowering your body temperature and calming your nervous system.
Enhanced Cognitive Function
Collagen isn’t highlighted often in discussions about cognitive function, but some studies suggest that glycine may enhance memory and cognitive performance. Maintaining a healthy brain is directly linked to a healthy mindset—a worthy goal you could support with proper nutrition.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations
As with any supplement or dietary change, it’s important to consider how collagen might affect you personally.
Allergies
Some collagen supplements are derived from sources that you may be allergic to, such as fish or shellfish. Always consult your healthcare provider before trying a new supplement, especially if you have allergies.
Quality Control
Not all collagen products are created equal. Some may contain fillers or low-quality ingredients. It’s advisable to research brands and read reviews before making a purchase.
Digestive Issues
For some individuals, taking collagen supplements may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort. Starting with a lower dosage can help you figure out what works best for your body.

This image is property of content.amymyersmd.com.
Conclusion
Your mental health is an intricate aspect of your overall well-being, influenced by a variety of factors—including nutrition. While the evidence linking collagen directly to improved mental health is still emerging, its benefits cannot be ignored. From supporting gut health to potentially enhancing mood and cognitive function, collagen may play a helpful role in your mental wellness journey.
As you venture into the world of nutrition and mental health, consider the impact of what you consume. Collagen, with its vast array of benefits, might just be the ally you need to foster a healthier, happier you.