Understanding Zero Trust Architecture: Enhance Your Cybersecurity Strategy. Discover Zero Trust Architecture: a smart approach to cybersecurity that ensures safety by verifying every user and device. Learn how it protects your data!
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model. It operates on a simple premise: never trust, always verify. Every access request is authenticated, authorized, and validated. This model emerged due to the increased complexity of security threats today. It applies to users, devices, and applications. All must prove their identity first.
Historically, networks had a perimeter. Once inside, users had broad access. This approach allowed threats to move freely. With Zero Trust Architecture, trust is not granted automatically. Each request is treated as if it comes from an open network. This reduces the risk of breaches.
Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
- Assume breach: Always act as if a breach could occur.
- Verify identity: Authenticate all users and devices.
- Least privilege: Give users the minimum access needed.
- Micro-segmentation: Divide networks into smaller segments for protection.
Key Components of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture consists of several crucial components. Each plays a role in its effectiveness. The primary components include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| User Identity | Ensures only authorized users gain access. |
| Device Security | Validates the security posture of each device. |
| Network Segmentation | Isolates parts of the network for better control. |
| Data Protection | Encrypts and secures sensitive information. |
The Role of Identity Management
Identity management is essential in Zero Trust Architecture. It ensures that only authorized users access sensitive data. Strong identity solutions use multi-factor authentication (MFA). This adds layers of security. MFA typically requires two or more verification methods. This might be a password, a phone verification, or a biometric scan.
Moreover, identity management can monitor user behavior. It tracks patterns that help detect anomalies. If a user behaves unpredictably, alerts are triggered.
The Importance of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is crucial for effective Zero Trust Architecture. It limits access to different network areas. Even if an attacker gains entry, they can’t move easily. Each segment has specific access controls.
Organizations can create these segments based on role or function. For example, the HR segment should not allow access to IT systems. This makes it harder for attackers to escalate their privileges.
Implementing Micro-Segmentation
- Identify application flows: Understand how applications communicate.
- Create policies: Define who can access what within segments.
- Monitor and refine: Keep an eye on access patterns and adjust accordingly.
Data Protection Strategies
Data remains a primary target for cyber attackers. In Zero Trust Architecture, protecting data becomes vital. Utilizing encryption is a common strategy. Encryption ensures data remains safe during transit and at rest.
Additionally, data loss prevention (DLP) solutions monitor sensitive data. These tools help prevent unauthorized access and leaks. They give organizations control over their data.
Encryption Methods for Data Security
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Symmetric Encryption | Uses the same key for encryption and decryption. |
| Asymmetric Encryption | Uses a pair of keys, public and private, for security. |
Endpoint Security in Zero Trust
Each device connecting to a network requires verification. Endpoint security is critical in Zero Trust Architecture. Protection extends to mobile devices, laptops, and servers.
Organizations use endpoint detection and response (EDR). This technology monitors endpoint activities for threats. When suspicious activity arises, alerts are sent for further analysis.
Challenges in Endpoint Security
- Device diversity: Different devices may require varying security measures.
- Remote work: Home networks may not be secure.
- Insider threats: Employees can inadvertently or deliberately cause breaches.
Zero Trust and Cloud Security
Many organizations use cloud solutions. The principles of Zero Trust Architecture apply equally in the cloud environment. Cloud applications often expand the attack surface. Therefore, continuous verification is paramount.
Cloud security relies on strong identity management. Access controls should be in place. Monitoring user activity in the cloud environment is critical. Utilize tools that identify unauthorized attempts to access cloud resources.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Use MFA | Strengthen access controls with multi-factor authentication. |
| Regular audits | Assess cloud configurations and access regularly. |
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Organizations must prioritize continuous monitoring. This concept ties into Zero Trust Architecture. Monitoring helps detect unauthorized access attempts immediately. Security Operations Centers (SOCs) play a vital role here.
Having an incident response plan ensures readiness for breaches. Organizations should regularly update and test this plan. Practicing incident response effectively prepares teams for actual events.
Key Steps in Incident Response
- Preparation: Develop a clear action plan.
- Identification: Detect potential security incidents.
- Containment: Limit the damage from a breach.
- Eradication: Remove the threat from the network.
- Recovery: Restore affected systems to normal operation.
Employee Training and Security Culture
Employee training is essential to support Zero Trust Architecture. Staff must understand security policies. They play a critical role in preventing breaches.
Regular training sessions focus on security awareness. Employees should learn about phishing, social engineering, and other attacks. Building a strong security culture helps organizations maintain vigilance.
Elements of Effective Training Programs
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Awareness Campaigns | Create ongoing discussions about cybersecurity. |
| Interactive Sessions | Use quizzes and simulations to engage employees. |
The Future of Zero Trust Architecture
The landscape of cybersecurity continues to change. Many organizations are adopting Zero Trust Architecture. The approach mitigates risks while enabling digital transformation. Future trends will likely involve more automation in security processes.
Artificial intelligence will also play a role. Using AI helps identify threats faster and more accurately. As cyber threats grow, so will the necessity for strong security frameworks like Zero Trust Architecture.
“Zero Trust Architecture is not just a concept; it is a necessity in today’s security environment.” – Edward Osinski
Anticipating Future Challenges
- Advanced persistent threats: Attackers becoming more sophisticated.
- Data privacy regulations: Organizations must comply with evolving laws.
- Integration challenges: Adapting existing systems to meet Zero Trust principles.
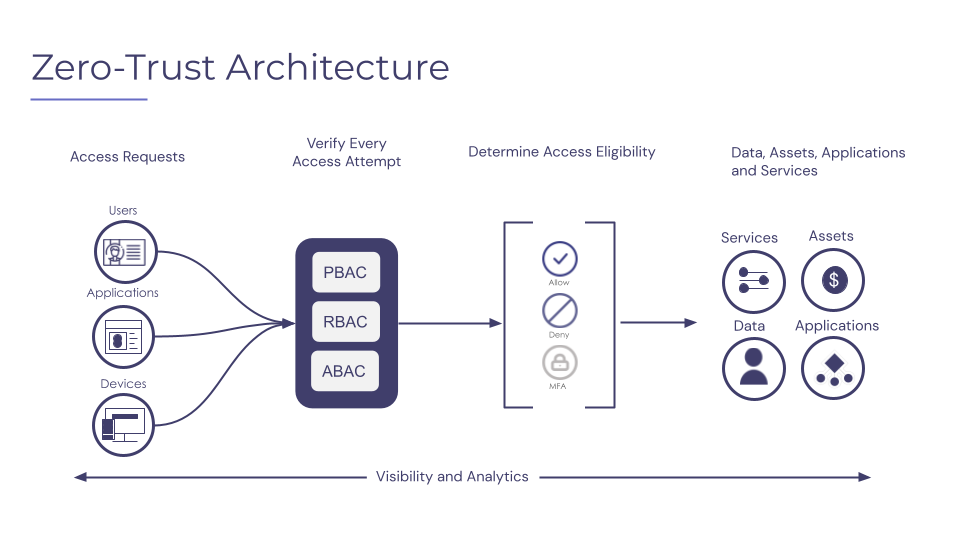
Industry Impact
The shift towards Zero Trust Architecture reflects a critical need. Organizations face frequent cyber threats. Data breaches disrupt operations and damage reputations. Traditional security measures often fall short. Businesses are vulnerable if they rely on perimeter security alone.
Analysts predict that the Zero Trust Architecture market will grow significantly. Companies invest in solutions that help protect their networks. The approach often focuses on identity verification. This ensures that users can only access the data they need.
Many industries benefit from adopting Zero Trust Architecture. Below are some examples:
- Financial services handling sensitive client data
- Health organizations protecting patient information
- Retail industries safeguarding customer transactions
Organizations gain better control over their data. They can monitor access and enforce policies effectively. A strong Zero Trust Architecture reduces the attack surface. This is vital as cyber threats increase.
Technological Innovations
Modern technology supports the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture. Cloud computing and advanced analytics play an important role. Organizations can leverage existing tools to implement this model efficiently.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enhance security measures. These technologies help identify unusual user behaviors. They adapt quickly to evolving threats. Using AI can streamline response times. This minimizes potential damage from attacks.
Furthermore, automation is a critical aspect. Routine security tasks can be automated. This allows security teams to focus on strategic priorities.
| Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | Scalable resources and improved access control |
| AI/ML | Better threat detection and response |
| Automation Tools | Increased efficiency in security management |
Integrating these technologies supports Zero Trust Architecture. Security teams become more proactive. They can anticipate and react to threats more effectively.
User Experiences
User experience remains a key factor in adopting Zero Trust Architecture. Organizations must ensure a balance between security and ease of access. Users may resist changes that complicate their workflows.
Streamlined processes help maintain productivity. Easy-to-use security protocols encourage user compliance. Providing clear guidance can enhance user interactions. Training employees on new security measures is essential.
- Educate users on secure practices
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) for ease of access
- Offer regular updates and support resources
Feedback is crucial. Organizations can adjust security measures based on user input. This leads to a better overall experience. Happy users are more likely to follow security protocols.
Implementation Challenges
Transitioning to Zero Trust Architecture presents challenges. Organizations face cultural and technical barriers. Teams often resist changes to their daily processes.
Financial constraints can also hinder progress. Upgrades to systems and tools require funding. Organizations must prioritize investments wisely. Developing a phased implementation plan can help. This approach allows them to allocate resources effectively.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Resistance to Change | Conduct workshops to address concerns |
| Budget Limitations | Adopt a phased implementation plan |
| Lack of Expertise | Invest in training or consult external experts |
Addressing challenges ensures smoother transitions. Effective communication keeps all stakeholders informed. This fosters a supportive environment for the new architecture.
Policy Development
Policies play a significant role in Zero Trust Architecture. Organizations need to define clear rules for accessing data. Policies must be consistent across all departments. This ensures a uniform approach to security.
The development of key policies requires input from multiple teams. Collaboration between IT, security, and management is crucial. These groups should regularly review policies to keep them up to date.
- Identify sensitive data and user roles
- Establish access controls based on user needs
- Implement monitoring to track compliance
Effective policy development reduces risks. It helps keep sensitive information secure. Regular audits also ensure compliance with established policies.
Case Studies
Studying real-world examples illustrates the benefits of Zero Trust Architecture. Various organizations have successfully implemented this model. Here are noteworthy case studies:
| Company | Industry | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Finance | Reduced data breach incidents by 50% |
| Company B | Healthcare | Enhanced patient data protection |
| Company C | Retail | Improved transaction security and customer trust |
These organizations faced challenges but found success. They demonstrated how effective Zero Trust Architecture can be.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, organizations will enhance their Zero Trust Architecture. New trends will shape how security is implemented. Increased reliance on remote work adds more complexity. Organizations need to secure remote access points effectively.
IoT devices pose another significant challenge. More endpoints mean broader attack surfaces. Integrating IoT security into Zero Trust Architecture becomes essential.
- Focus on micro-segmentation to control access
- Strengthen identity and access management (IAM)
- Implement continuous monitoring for real-time threat detection
Organizations must stay ahead of emerging threats. This proactive stance will bolster security features.
Training and Awareness
Training programs are vital for a successful transition to Zero Trust Architecture. Employees need to comprehend security practices. Awareness campaigns can help reinforce the importance of security.
Organizations should offer regular training sessions. These sessions ensure that employees understand the new protocols. They should include real-life scenarios to enhance learning.
| Training Format | Description |
|---|---|
| Workshops | Interactive sessions to engage employees |
| Webinars | Remote training options for global teams |
| e-Learning Modules | Flexible online courses for self-paced learning |
Regular assessments can gauge employees’ understanding. This method helps organizations identify knowledge gaps.
Quote on Zero Trust
“Adopting Zero Trust Architecture protects critical assets more effectively.” – Myles Hettinger
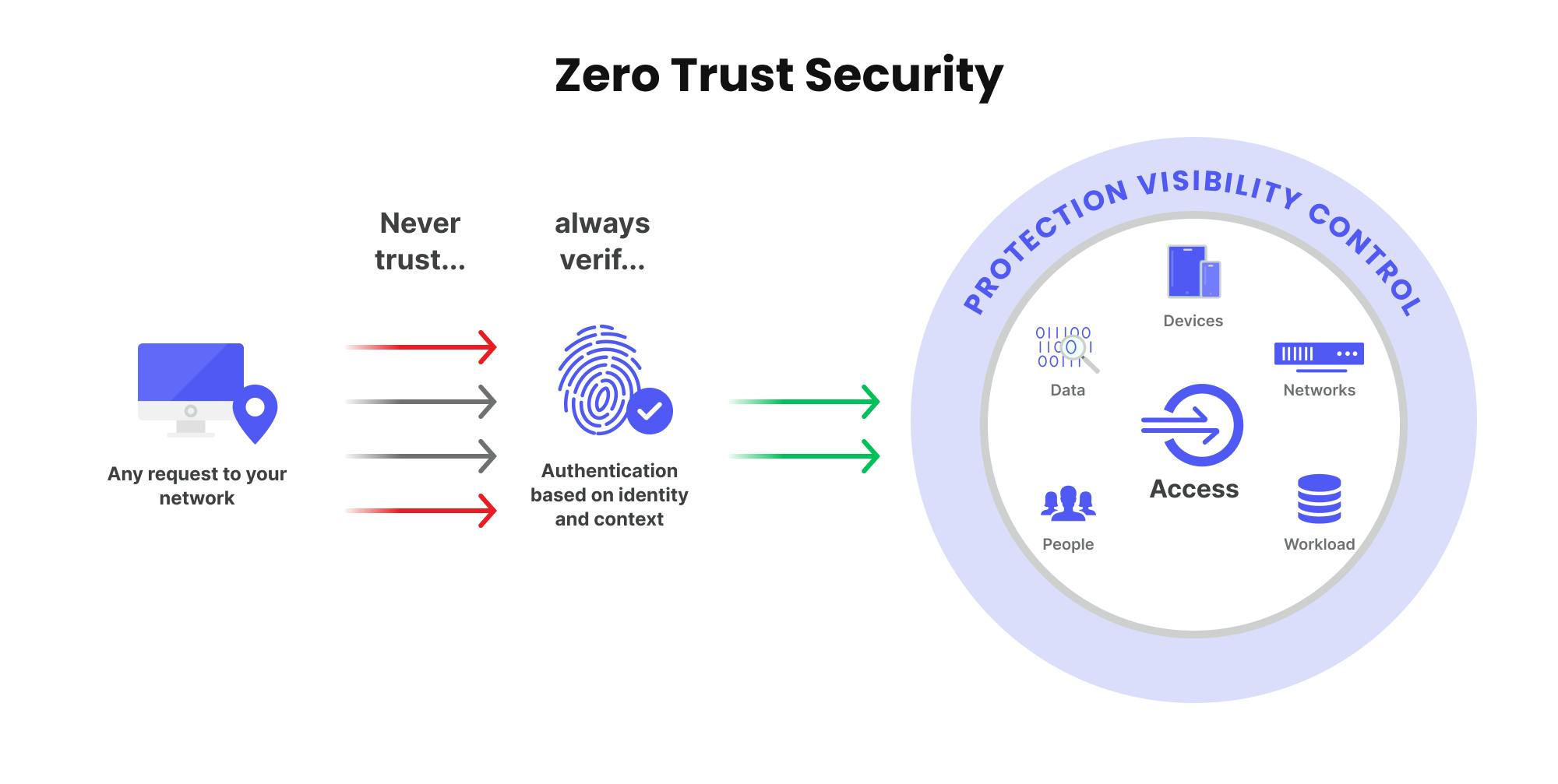
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust Architecture is a cybersecurity concept focused on eliminating trust assumptions. In traditional networks, once someone is in, they have access to everything. With Zero Trust Architecture, verification is mandatory. Every request must be authenticated and authorized. This method improves security by assuming that breaches can happen both inside and outside the network.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
- Never trust, always verify.
- Limit access to data and services.
- Implement micro-segmentation in the network.
- Secure all endpoints.
Challenges Faced in Implementing Zero Trust
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture presents several challenges. These can slow down the rollout process and impact overall strategy. Some common hurdles include budget constraints, resistance to change, and complexity of new technologies.
Budget Constraints
Many organizations find it difficult to budge funds for new cybersecurity solutions. Transitioning to a Zero Trust Architecture may involve considerable expenses. These include new tools, software, and training. Also, ongoing maintenance costs can increase over time. Without adequate financial support, the full benefits might not be realized.
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist changes to their daily routines. Trust is an essential part of workplace culture. When people feel monitored, it can create negativity. Training and clear communication about the benefits can ease concerns. Ensuring everyone understands the need for Zero Trust Architecture is vital.
Complexity of New Technologies
Organizations may struggle with the technical aspects of Zero Trust Architecture. New systems often come with a steep learning curve. Employees need adequate training to use these systems. Misconfigurations can lead to vulnerabilities. Proper planning and expert guidance help reduce these risks.
Success Stories of Zero Trust Implementation
Various organizations have successfully implemented Zero Trust Architecture. Their stories highlight confidence in this approach and tangible results.
Case Study: Financial Services Company
A major financial services firm faced data breach alerts. They shifted to Zero Trust Architecture to bolster security. This included strict identity verification and access controls. As a result, their security incidents decreased by 75%. Employees felt more secure in their work environment.
Case Study: Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider struggled to protect sensitive data. By adopting Zero Trust Architecture, they segmented the network. Each department had separate access levels. This minimized risk in case of breaches. The organization reported a substantial decrease in unauthorized access incidents.
Emerging Trends in Zero Trust Architecture
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, Zero Trust Architecture adapts to new threats and technologies. Some of these trends include AI integration, extended telemetry, and user behavior analytics.
AI Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being used to enhance Zero Trust Architecture. AI can analyze vast amounts of data quickly. This helps detect anomalies in real-time. Automated responses can address threats faster than manual processes. AI-driven security solutions improve overall efficiency.
Extended Telemetry
Extended telemetry allows organizations to monitor their environments better. By gathering data from various sources, teams can analyze user activities comprehensively. This insight enhances security posture. Organizations can respond swiftly to suspicious activities with more context.
User Behavior Analytics
User behavior analytics provide valuable insights into normal activities. By establishing a baseline, organizations can detect irregularities. It allows for quicker investigation of potential threats. As a part of Zero Trust Architecture, this helps mitigate risks effectively.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture Steps
Transitioning to a Zero Trust Architecture requires careful planning. Organizations can follow a series of steps to ensure success.
Step 1: Assess Current Infrastructure
Start by reviewing current security frameworks. Identify gaps in policies and technologies. Assess how to integrate Zero Trust Architecture principles. A thorough understanding of existing systems will guide improvements.
Step 2: Define Your Protect Surface
Identifying critical data and assets is essential. This includes applications, data, and services important to the organization. Understanding what needs protection helps in implementing effective security measures.
Step 3: Implement Micro-Segmentation
Using micro-segmentation minimizes risk by isolating segments within the network. Each segment can have different access policies. It reduces potential damage from breaches.
Step 4: Continuous Monitoring
Regular monitoring is key in a Zero Trust Architecture. Use advanced tools to track user behavior and access patterns. Continuous visibility into network activities enables quick detection of suspicious behaviors.
Tools for Zero Trust Architecture
Several tools support implementations of Zero Trust Architecture. Organizations can use these tools to strengthen their security.
| Tool Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Manage user identities and permissions. |
| Network Segmentation Tools | Implement micro-segmentation in networks. |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Protect endpoints from threats. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Monitor and analyze security events. |
Benefits of Zero Trust Architecture
Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture provides numerous benefits. Organizations experience enhanced security, reduced risk, and improved compliance.
Enhanced Security
With Zero Trust Architecture, organizations strengthen their security postures. By eliminating implicit trust, they limit access to critical data. This proactive approach reduces the probability of breaches.
Reduced Risk
The segmentation of networks decreases risk. If a breach occurs, it does not impact the entire organization. Isolation helps contain threats and prevents widespread damage.
Improved Compliance
Many industries have strict compliance requirements. Adopting a Zero Trust Architecture helps meet these regulations. Organizations can track access and data usage more effectively.
Common Misconceptions About Zero Trust
Misconceptions around Zero Trust Architecture can hinder successful adoption. Addressing these myths can clarify the requirements.
Myth: Zero Trust is Only for Large Companies
Some believe that only large enterprises need Zero Trust Architecture. In reality, all organizations, regardless of size, can benefit. Cyber threats affect all businesses, making security a priority.
Myth: Zero Trust is Too Complex
Another misunderstanding sees Zero Trust Architecture as excessively complicated. While there are challenges, a gradual approach can simplify transitions. Many tools available facilitate ease of implementation.
Quote on Zero Trust Architecture
“Adopting a Zero Trust approach is essential to secure your digital assets.” – Sarai Beatty
The Future of Zero Trust Architecture
The future of Zero Trust Architecture looks promising. As technology advances, new solutions will emerge. Organizations will continue to adjust their strategies. This ongoing evolution helps maintain security in a changing landscape.
Integration with Cloud Services
Cloud services are integral to modern business. As more organizations move to the cloud, Zero Trust Architecture will integrate with various platforms. This ensures secure access to cloud applications and data.
Collaboration with Artificial Intelligence
The collaboration between Zero Trust Architecture and AI will grow deeper. AI will enhance threat detection capabilities. Security systems will respond faster and more accurately.
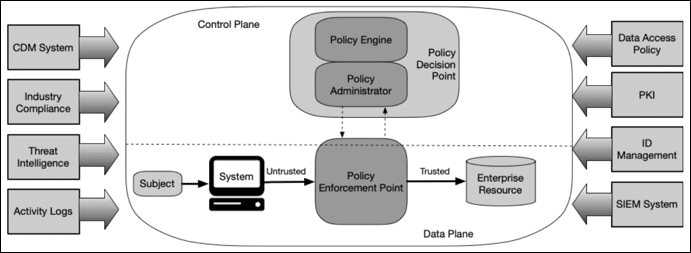
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model. It follows strict access controls. Every user, device, and network request is verified. Trust is never assumed. This approach helps limit risks. It counters various cyber threats effectively.
In this method, organizations treat each session as untrusted. Before granting access, verification is needed. This includes authentication and validation. The focus is on data protection and identity verification. It changes how organizations think about security.
Key Principles of Zero Trust
- Never trust, always verify.
- Limit access to data and resources.
- Assume breaches are imminent.
- Use micro-segmentation.
- Continuously monitor network traffic.
Recent Developments in Zero Trust Architecture
Many organizations adopt Zero Trust Architecture in recent years. Major tech companies provide enhanced solutions. They offer tools focused on identity management and access control. These tools aid businesses in securing their networks.
A report from 2022 shows that 70% of companies plan to implement Zero Trust Architecture. This growth is driven by increased cyber threats. New regulations also influence interest. Organizations need to comply with these regulations.
Cloud adoption is a significant factor. More companies move to the cloud and require advanced security. Zero Trust provides better protection in cloud environments. Tools like Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) play vital roles.
Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Security | Prevents unauthorized access. |
| Data Protection | Secures sensitive information. |
| Improved Compliance | Helps meet regulatory requirements. |
| Flexible Access | Supports remote work models. |
Case Studies of Zero Trust in Action
Several organizations have successfully implemented Zero Trust Architecture. Their experiences provide valuable insights.
One government agency adopted Zero Trust after a data breach. After implementation, they reported a 50% decrease in security incidents. Access controls were reinforced. This case highlights the effectiveness of Zero Trust Architecture.
Another case involves a large financial institution. They faced numerous cyber threats. After implementing Zero Trust, they improved their incident response time. Security teams responded faster to potential breaches.
Common Industry Challenges
While implementing Zero Trust Architecture, some common challenges arise:
- Complexity in integration with existing systems.
- Resistance from employees.
- High implementation costs.
- Continuous management and monitoring needs.
Organizations must address these challenges effectively. Education and training help employees adapt. Investing in tools can ease integration. Addressing concerns quickly enhances overall success.
Expert Opinions on Zero Trust Architecture
“Zero Trust Architecture is essential for modern cybersecurity. Organizations need to rethink their approach.” – Mr. Jimmie Mertz Sr.
Experts agree on the crucial role of Zero Trust Architecture in cybersecurity. Many believe it is necessary for all businesses. They suggest that traditional methods are no longer sufficient.
According to a leading cybersecurity analyst, the shift to Zero Trust is imperative. He stresses the importance of identity verification. “Access should be based on user identity, not location,” he states. This aligns with the philosophy of Zero Trust.
Tools that Support Zero Trust Deployment
| Tool | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Identity Access Management (IAM) | Verifies user identity. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds a layer of security. |
| Privileged Access Management (PAM) | Manages elevated permissions. |
| Endpoint Security Solutions | Protects devices from threats. |
The Role of Cloud Solutions in Zero Trust
Cloud solutions are central to Zero Trust Architecture. They facilitate remote access and scalability. Many organizations rely on cloud services. Cloud security integration is critical.
Key aspects include strong security policies and encryption. These measures ensure sensitive data remains protected. Policies must define access levels. Cloud solutions provide visibility into user behavior.
Additionally, cloud providers are enhancing security features. They offer advanced tools to implement Zero Trust principles effectively. This improvement is crucial for businesses with hybrid environments.
Cost Implications of Zero Trust Architecture
- Initial setup costs can be high.
- Compliance with regulations may require investment.
- Training employees incurs additional expenses.
- Ongoing maintenance costs must be budgeted.
Long-term savings can outweigh early costs. Reduced security incidents lead to fewer breaches. Organizations should view this as an investment in future safety.
How to Evaluate Zero Trust Solutions
Evaluating Zero Trust Architecture solutions requires careful consideration. Organizations must define their needs first. A thorough assessment will help identify the right tools.
Key factors to evaluate include compliance requirements. Look at scalability options and integration capabilities. Organizations should also consider user experience and cost. It’s essential to choose a solution that aligns with business goals.
Steps for Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| Assess Current Security Posture | Identify vulnerabilities and gaps. |
| Define Access Controls | Establish permissions for users and devices. |
| Implement Necessary Technologies | Choose tools that fit organizational needs. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Regularly evaluate user behavior and access. |
Future Outlook for Zero Trust Architecture
The future of Zero Trust Architecture looks promising. As cyber threats evolve, so must security strategies. More organizations will adopt this model. This growth leads to better security measures overall.
Advancements in technology will enhance Zero Trust solutions. Integration with technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) will improve threat detection. This will aid in proactive security measures, making organizations safer.
Training and Awareness for Successful Implementation
Culture plays a vital role in applying Zero Trust Architecture. Training employees is essential. They must understand the principles and practices.
- Provide regular training sessions.
- Educate teams on security best practices.
- Engage employees in security protocols.
- Conduct simulated attacks to test readiness.
Investing in training pays off. A security-aware workforce strengthens overall defense.
Definition of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model that requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources on a network. Unlike traditional security, it does not assume that users inside the network are trustworthy. Every access request is treated as a potential threat. This model relies on continuous authentication and stringent access controls to operate effectively. The primary goal is to protect data, applications, and services from both internal and external breaches.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
Several principles guide Zero Trust Architecture. These principles help organizations focus on protecting their assets in a systematic way.
- Never trust, always verify.
- Assume breach mentality.
- Least privilege access control.
- Micro-segmentation of networks.
- Continuous monitoring and logging.
These principles create a solid framework that enhances cybersecurity. Organizations adopting these principles can minimize risks associated with data breaches more effectively.
Practical Applications of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture finds application in various domains. Organizations use it for securing cloud environments, remote workforces, and more. Each application highlights the versatility of this security model.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Securing Cloud Access | Strictly controls access to cloud applications. |
| Remote Work Security | Ensures secure connections for remote workers. |
| Network Segmentation | Divides networks into smaller, secure sections. |
| Data Protection | Protects sensitive data through continuous monitoring. |
| Identity and Access Management | Employs strong authentication methods. |
These applications demonstrate how Zero Trust Architecture can be effectively implemented across various sectors, aiding in compliance and security.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture is not without its hurdles. Organizations often face several challenges in adoption.
- Complex integration with existing systems.
- High initial costs and resource requirements.
- Resistance to change from employees.
- Lack of skilled personnel.
- Difficulty in maintaining continuous monitoring.
Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning and commitment from all levels of the organization. A phased approach can ease the transition to a Zero Trust Architecture.
Technologies Supporting Zero Trust Architecture
A variety of technologies support the principles of Zero Trust Architecture. These tools help organizations implement the necessary security measures.
| Technology | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Enhances verification processes. |
| Identity and Access Management Systems | Manages user identities and access rights. |
| Encryption Technologies | Secures data in transit and at rest. |
| Endpoint Detection and Response | Monitors devices for suspicious activities. |
| Threat Intelligence Platforms | Provides data on potential threats. |
These technologies bolster the Zero Trust Architecture framework. They make it easier for organizations to be vigilant against cyber threats.
Future of Zero Trust Architecture
The future of Zero Trust Architecture looks promising as organizations continue to embrace this security model. Emerging trends indicate greater adoption of zero trust principles across various sectors. Companies realize that traditional security models fall short in protecting against modern threats.
- Increased use in hybrid cloud environments.
- Greater emphasis on user experience alongside security.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
- Improved regulatory compliance features.
- Collaboration across industries for best practices.
As more organizations implement Zero Trust Architecture, shared insights will drive innovation. This evolution will help security measures grow stronger.
Importance of Employee Training in Zero Trust Strategies
Employee training is crucial in adopting Zero Trust Architecture. Employees must understand their roles in maintaining security. They also need awareness of potential threats. Comprehensive training programs can bridge this gap.
| Training Focus | Description |
|---|---|
| Phishing Awareness | Teaches employees how to spot phishing attempts. |
| Safe Data Handling | Guides employees in managing sensitive information. |
| Incident Response | Educates on steps to take during security incidents. |
| Access Protocols | Clarifies the importance of following access protocols. |
| Regular Updates | Emphasizes staying current with security practices. |
With training, employees become a line of defense against threats. This engagement strengthens the organization’s Zero Trust Architecture.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Zero Trust Architecture
Organizations must conduct a cost-benefit analysis to assess adopting Zero Trust Architecture. While the upfront costs may be high, the long-term benefits can outweigh these investments. The analysis should consider various factors.
- Initial implementation costs.
- Ongoing maintenance and updates.
- Potential losses from security breaches.
- Compliance with regulations.
- Improvement in overall security posture.
Investing in Zero Trust Architecture can lead to significant savings over time. A stronger security stance reduces the risk of breaches and related losses.
Collaboration in Zero Trust Deployments
Collaboration plays a vital role in deploying Zero Trust Architecture. Stakeholders must work together to ensure success. Departments across an organization must unite for effective implementation. Collaboration fosters communication and coherence, which are essential.
| Stakeholder | Role |
|---|---|
| IT Department | Executes technical implementations. |
| Security Team | Monitors for security threats. |
| HR Department | Facilitates employee training. |
| Management | Supports policy and budget decisions. |
| End Users | Adheres to security protocols. |
In conclusion, a collaborative approach eases transitions. Everyone has roles that contribute to the success of Zero Trust Architecture.
“A holistic approach to security is necessary. Zero Trust encourages us to think differently about how we protect our assets.” – Adrien Stokes
Regulatory Compliance and Zero Trust Architecture
Regulations influence how organizations manage data. Zero Trust Architecture helps in achieving compliance with various standards. Organizations that adopt zero trust principles often find it easier to adhere to regulations.
- GDPR: Protects personal data.
- HIPAA: Safeguards health information.
- PCI DSS: Secures payment information.
- Sarbanes-Oxley: Provides financial transparency.
Utilizing Zero Trust Architecture improves compliance readiness. Organizations can secure data and mitigate risks more effectively.
Case Studies of Zero Trust Implementation
Examining case studies can provide insight into Zero Trust Architecture. Organizations have seen success using zero trust principles. These examples highlight practical applications and results.
| Company | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Financial Institution A | Reduced breaches by 60%. |
| Healthcare Provider B | Enhanced patient data security. |
| Retail Company C | Improved fraud detection systems. |
| Tech Firm D | Streamlined remote access for employees. |
| Manufacturing Company E | Strengthened supply chain security. |
These case studies illustrate the efficacy of Zero Trust Architecture. They provide concrete examples of successful implementations across different sectors.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Zero Trust
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) enhance the effectiveness of Zero Trust Architecture. These technologies can automate many security processes.
- Identify unusual patterns in user behavior.
- Predict potential threats based on past data.
- Streamline incident response processes.
- Provide real-time insights and alerts.
- Refine authentication processes through biometric analysis.
Integrating AI and ML into Zero Trust Architecture can lead to faster detection and mitigation of threats. This synergy can improve overall security posture significantly.
Integration with Existing Security Frameworks
Integrating Zero Trust Architecture with current security frameworks is crucial. Organizations can enhance their systems without complete overhauls. This integration process requires careful planning.
| Framework | Integration Approach |
|---|---|
| Network Security | Apply micro-segmentation techniques. |
| Identity Governance | Utilize least privilege access policies. |
| Endpoint Security | Deploy advanced threat protection solutions. |
| Cloud Security | Implement stringent access management. |
| Compliance Management | Ensure ongoing monitoring and reporting. |
Successful integration requires commitment and resources. Organizations should see improved security outcomes with a structured approach to Zero Trust Architecture.
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust Architecture is a cybersecurity model that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It requires strict identity verification for everyone and everything trying to access resources within a network.
Why is Zero Trust important?
Zero Trust is important because it minimizes the risk of data breaches by ensuring that no user or device is trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter.
How does Zero Trust differ from traditional security models?
Traditional security models typically focus on perimeter defenses, assuming that users or devices within the network are trustworthy. In contrast, Zero Trust assumes that threats can exist both inside and outside the network, requiring verification for all access attempts.
What are the core principles of Zero Trust?
The core principles of Zero Trust include continuous verification, least privilege access, micro-segmentation, and comprehensive visibility into all users and devices accessing the network.
What does least privilege access mean in a Zero Trust model?
Least privilege access means that users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems.
How does micro-segmentation work?
Micro-segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit lateral movement of threats. Each segment can have its own access controls and security policies.
What technologies support Zero Trust Architecture?
Technologies that support Zero Trust include identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication (MFA), endpoints security, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
How can organizations implement Zero Trust?
Organizations can implement Zero Trust by assessing their current security posture, identifying sensitive data and resources, enforcing access policies, and continuously monitoring for unusual activity.
What role does encryption play in Zero Trust?
Encryption is critical in Zero Trust as it helps protect data in transit and at rest, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains secure and unreadable without the proper keys.
Can Zero Trust work with existing security solutions?
Yes, Zero Trust can be integrated with existing security solutions. It enhances and complements traditional security measures by shifting the focus to user and device verification at all levels.
What challenges might organizations face with Zero Trust implementation?
Challenges can include resource limitations, resistance to change from employees, potential disruptions during implementation, and the need for comprehensive visibility and monitoring systems.
How does continuous monitoring fit into Zero Trust?
Continuous monitoring is essential in Zero Trust to detect and respond to threats in real-time, ensuring that any suspicious activity is identified and addressed promptly.
Is Zero Trust only for large enterprises?
No, Zero Trust is applicable to organizations of all sizes. Smaller businesses also benefit from implementing Zero Trust principles to improve their security posture against cyber threats.
What is the relationship between Zero Trust and cloud security?
Zero Trust is increasingly relevant for cloud security, as it helps organizations secure their cloud services by ensuring that all access is verified, regardless of where users or devices are located.
How does employee training contribute to Zero Trust?
Employee training is vital for Zero Trust, as it ensures that staff are aware of security policies, practices, and the importance of following protocols to minimize risks effectively.
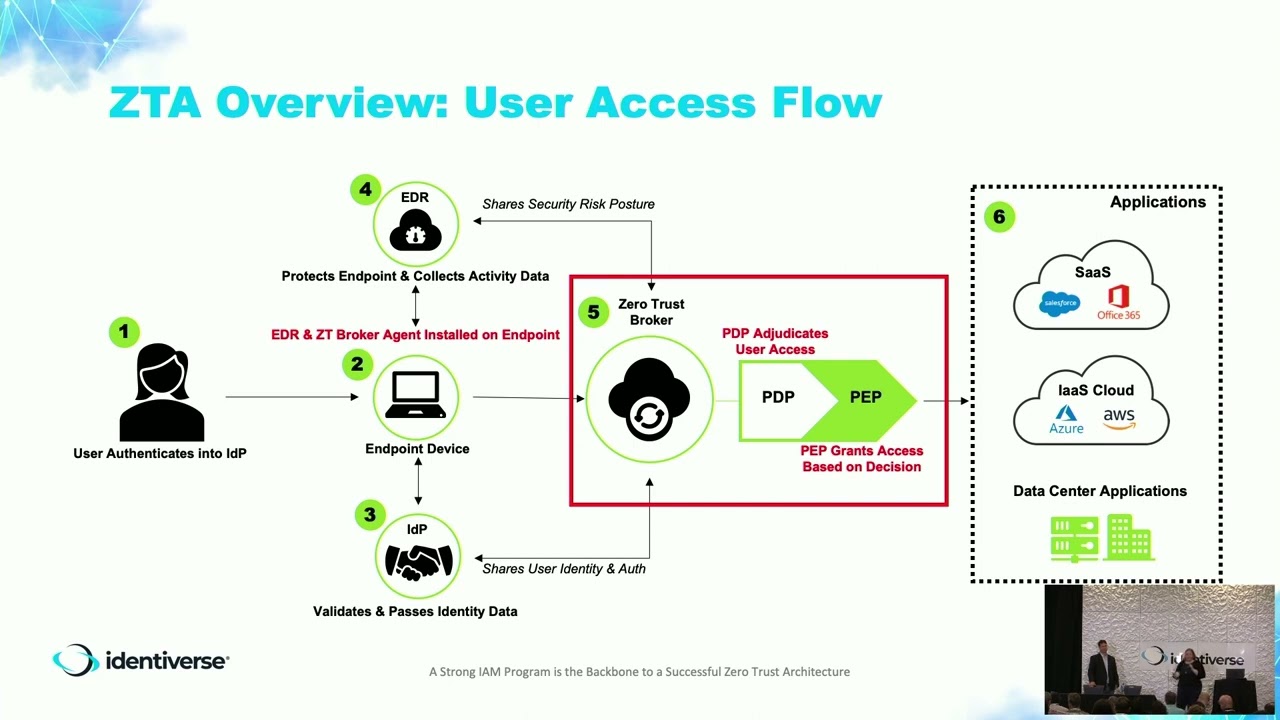
Conclusion
Adopting Zero Trust Architecture is essential for enhancing your cybersecurity strategy. By assuming that threats can come from anywhere, this approach ensures that every access request is verified. This means protecting your data and systems more effectively. Businesses of all sizes can benefit from implementing these principles. It’s about being cautious and proactive in today’s digital landscape. As cyber threats continue to rise, investing in Zero Trust can help in significantly reducing risks. Make sure to educate your team and regularly review your security measures for the best results. Protecting your assets starts with your awareness and action.